|
General
options:
Scale: this option allows
to change the size of the texture from a given scale factor. Rotation: this option
allows to change the orientation of the texture from a
given angle. Receive shadows: this
option allows to specify that the material can receive
shadows. Cast shadows: this option
allows to specify that the material can cast shadows. Fresnel reflection (for
PBR materials only): physical effect that make a dielectric
material (glass, plastic) fully reflective for tangential
rays. Thus, a pane of glass is transparent when it is
seen from the front and becomes more and more reflective
and less and less transparent when you look at it sideways.
The Fresnel reflection
option allows to simulate this effect for two material.
When the material is transparent with a refraction factor,
as the glass for example, the Fresnel reflection tends
to make the object silhouette darker. When the material
is opaque with a reflection coefficient, the reflection
is null in front of the object
but increases to the indicated value at the silhouette
of the object.

|

|
Without
Fresnel reflection |
With
Fresnel reflection |
- A material with
glazed parts must reflect light where it is transparent (because
there is material).
- A material representing
mesh does not reflect light where it is transparent (because there
is no material).
-
None: no texture mapping. |
-
Inherited: the mapping used is the one specified
in the texture definition document. |
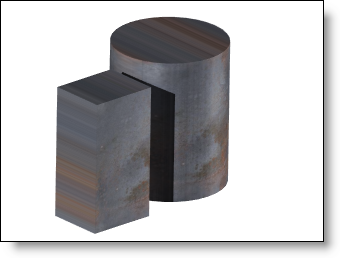
- Planar: the image
is plated on the object regarding a planar projection
to be able to minimize image deformations. Parameters
of this category are the same than Auto-axis
category. |
|
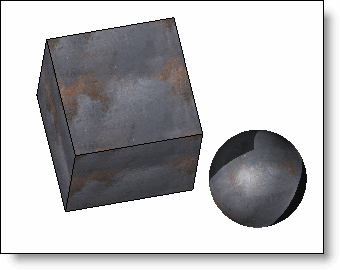
-
Auto-axis: the image is plated on the object in
the 3 orthogonal directions by minimized image deformations.
The parameters of this category are the same than Planar category. |
|
-
Cylindrical: the image is rolled around a cylindrical
object to be able to minimize image deformations. The
width of the image corresponds to the rolling, the height
will be applied regarding the cylinder height. |

|
-
Spherical: the image is rolled around a spherical
object to be able to minimize image deformations. The
width and the height correspond to the rolling on the
sphere. |

|
-
Edge: it is to be preferred for wood applications
to add textures on the edges. This mapping allows to keep
the same orientation along the edge faces. Recommended
for plane faces and cylindrical faces mainly. |
-
Parametric: this mode should be used when working
with FBX files with attached textures. TopSolid will then
use the mapping defined in the FBX model which specifies
the correspondence of each of the texture points on the
polyhedron.. |
- Transparency color. |
-
Index of refraction: indicates the deflection of
the light beams when they pass through the transparent
material. If this field is not filled, the material does
not produce refraction effects.

|

|
No
refraction |
Refraction index 1.5 |
|
-
Diffuse color: represents the base color independently
of the reflections. |
- Reflection
color. |

|
This
material is created from several maps (Albedo,
Roughness,
Metalness
,...) which can be defined manually (from a color
or a value) or with a texture document. Different
Internet resources (AmbientCG,
Adobe Substance 3D
Assets, Poliigon,
...) propose the download of PBR materials in which
you can find the different images allowing to create
the textures to be used in each map (you have to create
as many textures as there are maps/images available
in the downloaded PBR material). It is also necessary
to take care to give an identical width of texture
for each of the textures of a given material. This
first level of definition can be enriched with the
graph
editor of the map. |
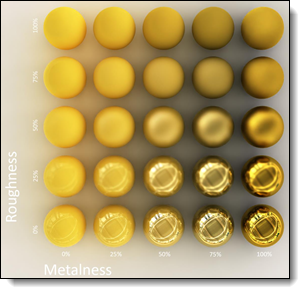
Albedo:
diffuse color of the material. Roughness: is used
to define the degree of roughness/mattness or gloss/glossiness.
The higher the value value is important, the more
the material will be mat (no reflection if roughness
at 100%). The lower
the value, the more brilliant the material will be. Metalness:
allows to define if the material is metallic
(iron, copper, gold, ...) or dielectric (glass, ceramic,
plastic, ...). Generally the value will be 100% or
0% if the material is metallic or non-metallic.
|
Link
between metalness and roughness |
|
Normal:
allows to give relief to the material as if
it was a real geometry (irregularity of a leather
for example). Depending on the Internet resources,
it is possible you may have 2 images to define the
normal, a DirectX image and an OpenGL image. In this
case you should use the OpenGL image. Opacity:
Opacity determines whether the object is transparent
or opaque. The darker the color the more transparent
the object will be. Transmission
glossiness:
indicates how much the light is scattered when
it crosses the interface of a transparent material.
At zero, the material is perfectly transparent. When
this value increases, the material becomes translucent. Ambient occlusion:
allows to give shading on some areas of the material
(on the stitches of a leather for example). Transmission scattering:
the transmission scattering color and the transmission
scattering length go together. This setting is similar
to the transmission glossiness, except that the effect
is volumetric. The transmission scattering color represents
the color of the particles inside the transparent
material, and the scattering length indicates the
distance a ray can travel before being absorbed by
a particle. This is useful for
simulating transparent liquids (like wine) where the
color is due to the particles in the liquid and where
the thickness of the material must be taken into account. |
|

 icon, then select the
icon, then select the  icon in Advanced
tab.
icon in Advanced
tab.