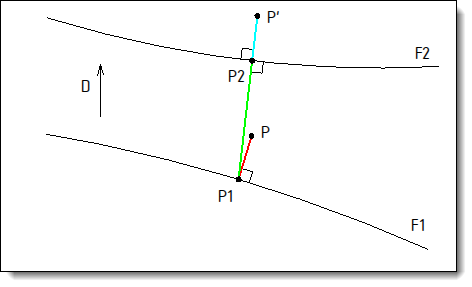
Example of computation of deformation point using the Nearest type for the projection (in red) and the matching (in green) and the Normal type for the expansion.
|
|
Shape on Shape Deformation |
This command allows to compute a deformation according to 2 surfaces and different types of projection and matching.
Let's take a point named P on the shape to deform, a source shape (F1) and a destination shape (F2).
The computation of the equivalent of the point P (named P') on the shape F2 is done in 3 stages:
Stage 1: Projection
The point P is projected on the shape F1 using to 2 modes (Parallel or Nearest), you get the point P1.
Stage 2: Matching
Then the point P1 is reported on the shape F2 using 3 modes (Parallel, Normal or Nearest), you get the point P2.
Stage 1: Expansion
Then the position of the point P' is obtained by moving the point P2 using 2 modes (Parallel or Normal), a scale factor can be applied as well.
 |
|
|
Example of computation of deformation point using the Nearest type for the projection (in red) and the matching (in green) and the Normal type for the expansion. |
Creation stages / Use:
Select the Construction > Deformations > Shape on Shape Deformation... command from the drop-down menu.
Select the source shape.
Select the destination shape.
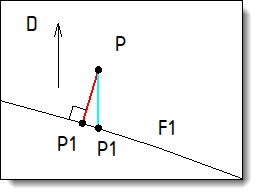
Choose the projection type of each point of the shape to modify on the source shape:
Parallel: the point P is projected on the shape F1 according to the given direction D.
Nearest: the point P is projected on the shape F1 according to the normal direction.
 |
|
|
In blue: Parallel projection type according to the direction D. in red: Nearest projection type |
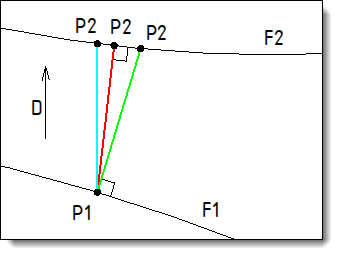
Choose the maching type between the source and the destination shapes:
Parallel: the point P1 is projected on the shape F2 according to the given direction D.
Normal: the point P1 is projected on the shape F2 according to a direction perpendicular to the shape F1.
Nearest: the point P1 is projected on the shape F2 according to the perpendicular direction.
 |
|
|
In blue: Parallel projection type according to the direction D. In green: Normal projection type in red: Nearest projection type |
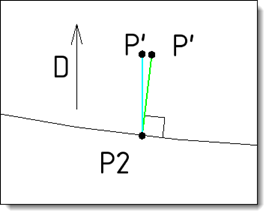
Choose the expansion type of each point of the deformed shape according to the destination shape:
Parallel: the position of point P' is computed by applying a translation of the point P2 according to the given direction D.
Normal: the position of point P' is computed by applying a translation of the point P2 according to the perpendicular direction with the shape F2.
 |
|
|
In blue: Parallel projection type according to the direction D. in red: Nearest projection type |
Select the deformation direction. The first face intersecting this direction will be used for computing the deformation, it is recommended to use surfaces instead of solid.
|
|
The initial volume of the shape is not preserved after deformation. |
Available options:
Display:
|
|
You can select a point on the shape to deform in order to display its final position. |
Example:
|
|
|
|
Source shape: the yellow plane at the bottom Destination shape: the blue wavy surface on top. |
Deformation result |