
|
The decimal
separator used is the one defined in the regional options in Windows (accessible via Start
> Settings > Control panel > Regional and Language options).
A value is validated (and moving on to next input field) via
the Tabulation
key. |
|
|
An
integrated calculator allows you to enter a simple formula or
parameter-based expression: |
|

|
See the
paragraph Operators and integrated functions
of the calculator for more detail. |

|
Formulas are not conserved when prefixed by the "#"
sign, only their result is conserved.
E.g.: Parameter h
equals 10
If you enter: 15
+ h or =15 + h
you will get: 25
(15 + h), the formula is kept and displayed.
If you enter: #15
+ h you will get: 25,
the formula is calculated but not kept. |
|
|
An input
error or an incomplete formula will display an exclamation point
and your input will not be validated:
|

|
Rolling
the cursor over the exclamation point displays a message indicating
the field containing the error.
|
|
|
The button
 displays the following drop-down menu which
allows you to recover a value by selecting an item in the graphic
zone or to select a parameter. displays the following drop-down menu which
allows you to recover a value by selecting an item in the graphic
zone or to select a parameter. |
|
|
Entered value: |
This is
the default mode, the value is entered by the keyboard. |
Measured value: |
The value
is measured by selecting an item in the graphic zone, there is
no link. |
Associative value: |
Idem "Measured value"
with a link to the selected item. |
|
|
The middle
section of the dialog allows you to create specific "on the
fly" parameters, i.e. the parameter was not created initially,
but will be created from the function. The different parameters
are: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
The last
section of the dialog allows you to create a parameter "on
the fly", i.e. the parameter was not created initially, but
will be created from the function. The different parameters are: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Function |
Description |
pi |
3.1415926535897932385 |
|
|
abs(x) |
Absolute
value |
|
|
sqrt(x) |
Square
root |
exp(x) |
Exponential |
ln(x) |
Naperian
logarithm |
log(x) |
Decimal
logarithm |
|
|
cos(x) |
Cosine
of an angle |
sin(x) |
Sine
of an angle |
tan(x) |
Tangent
of an angle |
|
|
acos(x) |
Arc
cosine of an angle |
asin(x) |
Arc
sine of an angle |
atan(x) |
Arc
tangent of an angle |
atan2(y;
x) |
Arc
tangent 2 arguments |
|
|
involute(x) |
Involute
of an angle. Result is a factor.
Corresponds to the operation "
tan(x) -(x*pi)/180 " |
inverseinvolute(x) |
Inverse
involute of a factor.
Result is an angle |
|
|
floor(x;unit) |
Conversion
from real by rounding to the lower value.  |
round(x;unit) |
Conversion
from real by rounding to the nearest value.  |
ceil(x;unit) |
Conversion
from real by rounding to the higher value.  |
|
|
val(text) |
Conversion
from text to number.  |
|
|
isnull(x) |
Returns
1 when the value of a real or a string is empty.
Example:
The value of the Diam
parameter is: when(isnull('Text 1');"-";"Ø"&'Text
1')
If Text
1 is empty then Diam
= -
If Text
1 is 16 then Diam
= Ø16 |
|
|
min(x;
y; ...) |
Returns
the minimum value between n values (n must be greater than or
equal to 2). |
max(x;
y; ...) |
Returns
the maximum value between n values (n must be greater than or
equal to 2). |
when(condition;
x; y) |
Returns
the x value if the condition is true and the y value if the condition
is false.  |
|
|
x&&y |
Corresponds
to the logical Operator AND : returns 1 if x and y conditions
are true.
It is possible to cumulate arguments
like for example : x&&y&&z |
x||y |
Corresponds
to the logical Operator OR : returns 1 if x or y conditions is
true.
It is possible to cumulate arguments
like for example : x||y||z |
! |
Different
from : x ! y returns 1 if x is different from y and returns
0 if x = y. When using in a parameter, select factor
while there is no unit. |
|
|
x==y |
Returns
1 if x = y |
x>=y |
Returns
1 if x > ( or equal) y |
x>y |
Returns
1 if x > y |
x<=y |
Returns
1 if x < (or equal) y |
x<y |
Returns
1 if x < y |
|
|
@'x'.y |
Retrieves
the value of the parameter y contained in the local
part or local
assembly named x.
Example: for a local part named Part 1 <155> containing
a parameter Dia, the expression
to enter will be @'Part 1 <155>'.Dia |
Function |
Description |
Example |
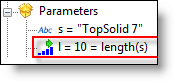
length(s) |
Get the number of characters of a string s. |
N=length("TopSolid")
is
equal to 8 (N is
an integer parameter). |
|
 |
|
|
|
|
left(s;n) |
Get the n first characters of a string s. |
C=left("TopSolid";3)
is
equal to "Top"
(C
is a text parameter). |
|

|
|
|
|
|
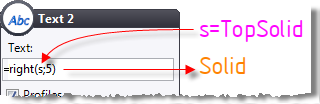
right(s;n) |
Get the n last characters of a string s. |
C=right("TopSolid";5)
is
equal to "Solid"
(C
is a text parameter). |
|
|
|
|
|
|
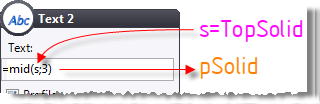
mid(s;m) |
Get the last characters of a string s starting from the
index m. |
C=mid("TopSolid";3)
is
equal to "pSolid"
(C
is a text parameter). |
|
|
|
|
|
|
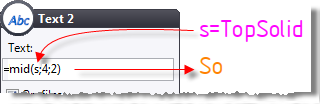
mid(s;m;n) |
Get the n characters of a string s starting from the index
m. |
C=mid("TopSolid";4;2)
is
equal to "So"
(C is
a text parameter). |
|
 |
|
|
|
|
& |
Merge (add) of strings |
S1="TopSolid"
and S2="great"
are 2 text parameters.
C=S1&" is "&S2
is
equal to "TopSolid
is great" (C is
a text parameter).
|
|

|
|
|
|
|
& |
Retrieve the value of a real
parameter |
L=20mm is a real parameter.
C="The length is: "&L
is equal to "The length
is: 20mm" (C
is a text parameter). |
|

|
|
|
|
|
format(v;f) |
Format the numerical value
v according to the f format.
Syntax
:
- 0 or
#: use # to
not display the integer value when it is equal to zero and
use 0 to
always display it.
- Optionally
.000…0
or
.###...#: the number of 0
or
#
symbols
gives the number of digits to display. With 0,
symbols, the number of digits is respected even with zeros
if needed. With #
symbols,
the zeros are not displayed if it is not necessary.
- Optionally
U: allows to display the unit
symbol.
|
C
is a text parameter:
C=format(0.5mm;
"0.00") is equal to "0.50"
C=format(0.5mm;
"#.00") is equal to ".50"
C=format(1.5mm;
"0.00") is equal to "1.50"
C=format(2.567mm;
"0.00") is equal to "2.56"
C=format(2.567mm; "0.##")
is equal to "2.56"
C=format(1.5mm;
"0.##") is equal to "1.5"
C=format(2.567mm,
"0.##U") is equal to "2.56mm"
C
is a text parameter and
D is the diameter of a cylinder (real)
equal to 35.6mm
C="Ø
of the rough cylinder: " & format(ceil(D;1mm);"0")
is equal to "Ø of the rough
cylinder: 36" |


![]()

 displays the following drop-down menu which
allows you to recover a value by selecting an item in the graphic
zone or to select a parameter.
displays the following drop-down menu which
allows you to recover a value by selecting an item in the graphic
zone or to select a parameter.






