|
In the upper section
is the appearance preview which is updated when modifying informations
entered below:
Select the specularity type.
Plastics reflect the light without modifying it, while a metal
colors the reflected light. The Custom
type allows to define a specular color which can be useful
to define a tinted mirror. For other kind of specularity types,
the specularity color cannot be changed and the dialog is
grayed. Select the Specular shininess
which indicates the quantity of reflected light relative to
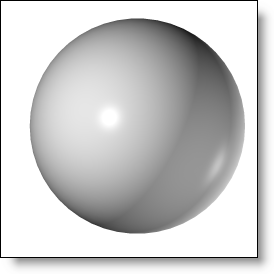
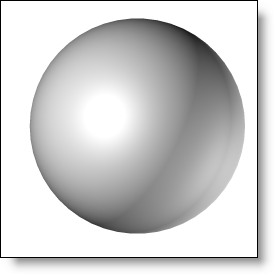
the incident light. Select the specular spreading
which indicates the gap between the real reflection of the
light relative to the perfect light. The more the material
surface is rough, the more the specular spreading is important.
|
|
Spreading
2% |
Spreading
20% |
Select the reflection coefficient
which indicates the quantity of light coming from other objects
of the scene and reflected by the material. Contrary to the
specular shininess which concerns the light reflections (primary
lighting), the reflection coefficient concerns object reflections
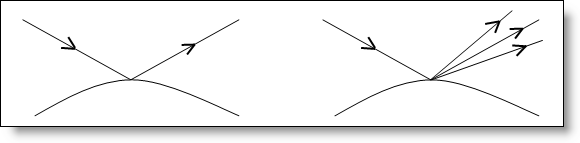
(secondary lighting). Select the reflection spreading
angle which indicates if the light is reflected
not only in one direction, but around an average direction
with some angular dispersion. Note that except for mirrors,
reflecting materials do not reflect the light perfectly. The
surface finish can give a frosted effect to the material.
The reflection is generally small (some degrees) because above
a certain value, the reflection is blurred enough and the
effect is no more visible (scattering material).
|
Perfect
reflection |
Reflection
with dispersion |
Choose the Fresnel reflection
which is a physical effect that make a dielectric material
(glass, plastic) fully reflective for tangential rays. Thus,
a pane of glass is transparent when it is seen from the front
and becomes more and more reflective and less and less transparent
when you look at it sideways.
The
Fresnel reflection option allows to simulate this effect for two
material. When the material is transparent with a refraction factor,
as the glass for example, the Fresnel reflection tends to make
the object silhouette darker. When the material is opaque with
a reflection coefficient, the reflection is null in front of the
object but increases to the indicated
value at the silhouette of the object.

|

|
Without
Fresnel reflection |
With
Fresnel reflection |
Select the specular color
to define for example a tinted mirror. Select the diffuse color
which represent base color without reflects. Texture:
select a bump
texture from the drop-down list. A texture document has
to be opened. Also select the
transparency
coefficient which indicates the quantity of lights
passing through the finishing. |

 icon, then select the finishing document type in Special tab.
icon, then select the finishing document type in Special tab.